When you change a URL in WordPress or remove a page, visitors and search engines can hit a 404 error instead of the content they expect. Redirects solve this by sending each old URL to the best new destination, preserving your rankings and user experience.
In this guide you’ll learn how to create 301 and 302 redirects in WordPress using a plugin, .htaccess rules, and best practices used on real‑world sites.
Quick answer on how to redirect URLs in WordPress
- For most sites: install the free Redirection plugin, then go to Tools → Redirection → add a 301 redirect from the old URL to the new URL.
- If you’re on Apache/LiteSpeed and prefer server rules: add a 301 redirect in your .htaccess file.
- After setting it up: test the status code (301/302) and update internal links to point directly to the new URL.
Which method should you use?
- Use a plugin (best for most WordPress users): easiest, safer, supports logs and bulk rules.
- Use .htaccess (Apache/LiteSpeed only): fastest at the server level, but easy to break if you make a typo.
- On Nginx or managed hosting: use your host’s redirect tool or server config (not .htaccess).
Understanding redirects and their importance
Redirects automatically send visitors and search engines from one URL to another. They’re crucial for:
- Preserving SEO rankings: They instruct search engines to transfer “ranking power” from old URLs to new ones.
- Enhancing the user experience: They prevent visitors from encountering 404 errors by guiding them to relevant content.
- Managing site changes: They facilitate smooth transitions during site migrations, URL restructuring, or content updates.
Types of redirects
Different types of redirects serve specific purposes. Here are several common types:
301 Permanent Redirect
- Indicates that a page has permanently moved to a new location
- Passes full link equity (ranking power) to the redirected page
- The most commonly-used redirect for SEO purposes
302 Found
- Indicates that a page has temporarily moved to a different location
- Tells search engines to keep the original page indexed
- Does not pass link equity to the new URL
307 Temporary Redirect
- Similar to a 302 redirect, but adheres strictly to the HTTP/1.1 specification
- Ensures that the request method remains unchanged
308 Permanent Redirect
- Functions like a 301 redirect, but preserves the request method
- Used in specific cases where POST requests need to be maintained
How to redirect a URL using a plugin
If you prefer a user-friendly approach, WordPress plugins are a great option. The Redirection plugin is one of the most popular tools, so let’s explore how to use it for redirects:
Installing the Redirection plugin
- Navigate to the WordPress dashboard.
- Go to Plugins → Add new plugin.
- Search for Redirection.
- Click Install Now, then Activate.
Configuring the plugin
- After activation, go to Tools → Redirection.
- Complete the setup wizard to configure basic settings.
Adding a new redirect
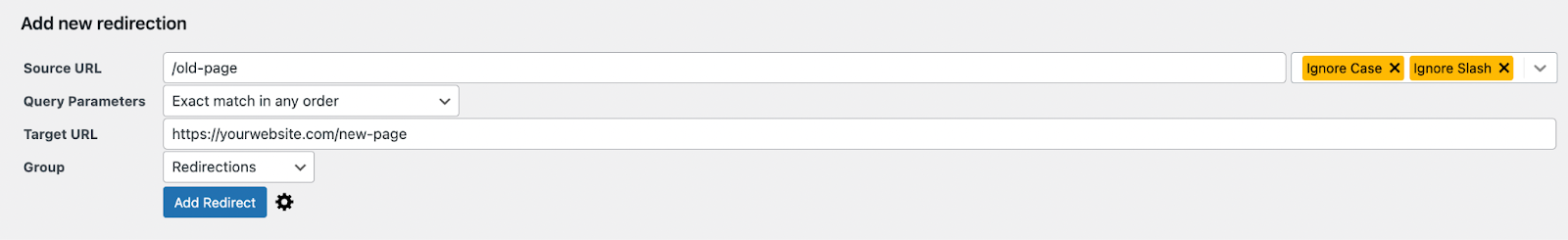
- In the Redirects tab, you’ll see a section titled Add new redirection.
- In the Source URL field, enter the URL path you want to redirect (e.g., /old-page).
- In the Target URL field, enter the full URL of the destination page (e.g., https://yourwebsite.com/new-page).
- Select the Redirection Type (e.g., 301 for permanent).
- Click Add Redirect to save the changes.
Additional features of the Redirection plugin
- 404 error logging to identify broken links
- Support for query parameter management
- Redirect grouping for better organization
How to redirect a URL using the .htaccess file
For those comfortable working with code and seeking more control, the .htaccess file provides a powerful method for setting up redirects. This is a configuration file used by the Apache web server to manage server behavior, including redirects.
Here’s how to create a redirect using the .htaccess file:
Accessing the .htaccess file
- Locate the .htaccess file:
- Connect to your website’s server using an FTP client or your hosting provider’s file manager.
- Navigate to the root directory of your WordPress installation (usually public_html).
- Ensure that hidden files are visible if you don’t see the .htaccess file.
- Back up the .htaccess file:
- Download a copy of the .htaccess file to your local machine before making any changes.
Adding redirect rules
- Open the .htaccess file:
- Use a plain text editor to open the .htaccess file.
- Add redirect rules:
- To add a 301 permanent redirect, insert the following line:
Redirect 301 /old-page https://yourwebsite.com/new-page- Replace /old-page with the old URL path and https://yourwebsite.com/new-page with the full destination URL.
- To redirect an entire directory, use the RewriteEngine module:
RewriteEngine On
RewriteRule ^old-directory/(.*)$ /new-directory/$1 [R=301,L]- This rule redirects all content from old-directory to new-directory while preserving the rest of the URL structure.
- Save and upload the .htaccess file:
- After adding the necessary redirect rules, save the .htaccess file.
- Upload the modified file back to your server, replacing the existing .htaccess file.
How to test your WordPress redirect
- Open the old URL in an incognito or private window and confirm it loads the intended destination.
- Use an HTTP status checker to make sure the response is 301 or 302.
- Verify that there is only a single redirect hop from the old URL to the final URL, not a chain of several redirects.
Best practices for managing redirects
Use the appropriate redirect type
- Apply 301 redirects for permanent changes to maintain SEO value.
- Use 302 or 307 redirects only for temporary moves.
Avoid redirect chains
- Ensure that URLs redirect to the final destination without multiple intermediate redirects.
- Redirect chains can slow down page load times and dilute SEO value.
Regularly monitor redirects
- Periodically review your redirects to ensure they’re functioning correctly.
- Use tools like Google Search Console to check for redirect issues.
Update internal links
- Instead of relying on redirects, update internal links to point directly to the new URLs.
- This reduces unnecessary redirects and improves site performance.
Troubleshooting common redirect issues
Redirect loop detected
- Occurs when a redirect sends visitors back to the same page in an infinite loop.
- Solution: Check the .htaccess file and plugin settings for conflicting rules.
Redirects not working
- Some servers require mod_rewrite to be enabled for .htaccess redirects to function.
- Solution: Confirm with your hosting provider that mod_rewrite is active.
404 errors after implementing redirects
- The target URL may not exist or may have a typo.
- Solution: Double check the destination URL in the redirect settings.
Final thoughts on WordPress redirects
Page redirects ensure that visitors and search engines can navigate your website without disruption. Whether you use a plugin or manually configure the .htaccess file, selecting the right method depends on your technical comfort level and site needs.
By following best practices and monitoring your redirects regularly, you can maintain SEO rankings, enhance the user experience, and prevent common redirection issues.
Simplify WordPress management with Jetpack
Managing redirects is just one aspect of maintaining a WordPress site. To streamline tasks and enhance overall efficiency, Jetpack offers a comprehensive suite of tools tailored for WordPress users. Developed by Automattic, the people behind WordPress.com, Jetpack integrates seamlessly into your site, providing features that bolster security, performance, and growth.
Comprehensive security features
Jetpack protects your site with features like real-time backups, malware scanning, and spam protection. These tools safeguard your content and maintain your site’s integrity.
Performance optimization
To enhance site speed and user experience, Jetpack offers a free content delivery network (CDN) that optimizes images and static files. This leads to faster load times and improved performance.
Growth and engagement tools
Jetpack’s suite includes tools designed to grow your audience and engage visitors. Features like automated social media sharing, site statistics, and SEO tools expand your reach and help you better understand user behavior.
Simplified site management
With Jetpack, managing your WordPress site becomes more efficient. Its centralized dashboard allows for easy oversight of site maintenance tasks, reducing the need for multiple plugins and simplifying site administration.
Learn more about Jetpack here: https://jetpack.com/
Frequently asked questions
What is the difference between a 301 redirect and a 302 redirect?
A 301 redirect tells search engines that a page has moved permanently to a new location. When you use this type, Google transfers the ranking power and trust from the old URL to the new one. You should use a 301 redirect when you delete a post or change your permalink structure forever.
A 302 redirect tells search engines that the move is only temporary. You use a 302 redirect when you are updating a page or running a short test. It keeps the original page indexed in search results because Google expects the original URL to come back soon. Choosing the right one ensures you do not lose your search rankings by mistake.
Will setting up redirects hurt my SEO rankings?
Redirects usually help your SEO rather than hurt it. When you delete a page without a redirect, visitors see a 404 error page. This signals to Google that your site has broken links or missing content. A proper 301 redirect solves this by sending users to a relevant page instead.
However, you can hurt your rankings if you create too many redirects or set them up incorrectly. A common mistake involves chaining redirects together so that one link leads to another and then another. This slows down your site and can confuse search engine bots. Always try to redirect directly from the old URL to the final destination in a single step.
Is it better to use a WordPress plugin or edit the .htaccess file?
Using a plugin is the best choice for most website owners because it is safer and easier to manage. Plugins like Redirection handle the technical code for you and let you manage links from your WordPress dashboard. This method reduces the chance that you will break your site by typing the wrong code.
Editing the .htaccess file is a method for advanced users who are comfortable with server files. It can be slightly faster for performance because the server processes the redirect before loading WordPress. If you are not a developer, stick to a reliable plugin to avoid taking your site offline accidentally.
What is a redirect loop and how do I fix it?
A redirect loop happens when URL A points to URL B, but URL B points back to URL A. The browser tries to load each page endlessly until it gives up and shows an error message saying “too many redirects.” This often occurs if you have conflicting rules in your redirection plugin or your server settings.
To fix this issue, you should clear your browser cache first to make sure you are not seeing an old version of the page. Next, check your active redirects and look for duplicates. If you recently switched your site from HTTP to HTTPS, make sure your settings do not force the pages to bounce back and forth between the secure and non-secure versions.
Do I need to keep my 301 redirects active forever?
You should keep a 301 redirect active for as long as possible. Google recommends keeping them in place for at least one year. This gives search engines enough time to crawl your site and update their index with the new URL. It also ensures that users who clicked on old links from other websites still find your content.
If you remove the redirect too soon, those old links will break and turn into 404 errors. Since redirects do not use much server space, it is usually safer to leave them alone indefinitely unless you have thousands of them slowing down your database.
How do I redirect an entire website to a new domain?
Redirecting a whole domain requires a server-level wildcard redirect. This rule tells the browser that every single page on the old site corresponds to the same path on the new site. For example, oldsite.com/contact will automatically go to newsite.com/contact.
You typically set this up in your hosting control panel or the .htaccess file rather than using a standard WordPress plugin. After you set up the technical redirect, you must use the “Change of Address” tool in Google Search Console. This notifies Google that your site has moved so it can update its search results faster.
Can too many redirects slow down my WordPress site?
Having a few dozen or even a few hundred redirects will not noticeably slow down your site. However, having thousands of redirects can affect performance if they are all stored in your WordPress database. Every time a visitor loads a page, the database has to check that list to see if a redirect exists. If the list is massive, this checking process takes time.
Redirect chains are even worse for speed. If a user has to jump through three different URLs to get to the content, the page will feel slow and sluggish. Regularly check your redirect list and delete old rules that no longer get any traffic.
What is a wildcard redirect and when should I use it?
A wildcard redirect allows you to move a group of URLs that share a common pattern without creating a separate rule for each one. This is very useful if you change the structure of your permalinks.
For instance, if you decide to remove the year from your blog post URLs (changing /2023/post-name to just /post-name), a single wildcard rule can handle every post at once. This saves you from typing out hundreds of individual redirects manually. You should only use this method if the new URL structure follows a consistent pattern that matches the old one perfectly.
How can I verify that my redirect is working correctly?
You should not rely only on your own browser to test a redirect because browsers save old data in their cache. The best way to test is by using an “Incognito” or “Private” window where no history is saved. Type in the old URL and watch the address bar to see if it changes to the new one immediately.
You can also use free online tools called HTTP header checkers. These tools show you the exact code the server sends back. You want to see a “301 Moved Permanently” status followed by the new URL. If you see a 404 code instead, the redirect is not working.
Why is it important to redirect HTTP to HTTPS?
Redirecting HTTP to HTTPS ensures that all visitors have a secure connection to your website. If you install an SSL certificate but do not set up a redirect, your site might still be accessible via the insecure HTTP version.
This confuses search engines because they might see two versions of your site as duplicate content. It also shows a “Not Secure” warning to your visitors in their browser bar. A proper redirect forces every visitor to the secure version automatically. This protects user data and is a verified ranking factor for Google, meaning it can help your site rank higher.
