As technology continues to advance, all of us are ever-more reliant on the internet for just about every aspect of our lives. Unfortunately, that means that cybercriminals also have seemingly endless opportunities to take advantage of us, always looking for ways to steal money, personal information, or account access data.
According to data company IPSOS in a survey conducted for Wells Fargo, almost one in three Americans said they were a victim of online financial fraud or cybercrime in 2023. Those over the age of 35 were more likely to fall victim to online fraud than the younger generation.
The good news is more, and more people are aware of common scams and are increasingly cautious in their online activities. To help you build your online vigilance skills, here are some guidelines on how to know if a website is safe to buy from:
2-minute checklist to assess whether a site is safe
If you’re about to enter card details and you’re thinking “is this store legit?”, use this 2-minute checklist first. If the site fails any 2 red-flag checks (weird payments, no real contact info, policy looks copied, or it’s flagged by a safety checker), don’t buy. Use a credit card when possible for better dispute protections.
- Site loads over HTTPS and shows no browser warning
- Real contact info (phone + address) that matches the company name
- Clear refund/returns + shipping policy that reads brand-specific
- Reviews exist outside the site (not just testimonials)
- Domain isn’t brand-new or hiding behind suspicious details
- Payment methods look normal (credit card, reputable processors)
- Not flagged by a malware/phishing checker
How to check if a website is secure
As a consumer, you have several ways to check to see if a website is safe to browse and buy from. Here is a list for you to keep handy that will help you avoid falling victim to scams:
1. Check for HTTPS in the URL
A quick peek at your browser bar — where you type in a website’s address — can immediately show if the site you are on has a secure sockets layer or SSL certificate. The “s” that comes after “http” is an easy indicator of an SSL certificate, which is a digital certificate that encrypts both personal information and financial data sent between a website and browser.
2. Note a padlock icon in the address bar
Note: Modern browsers may not show a padlock anymore (Chrome replaced it with a “tune”/site controls icon). Click the icon next to the URL to view connection and site information. You’re looking for confirmation that the connection is encrypted (HTTPS) and for any browser warnings about an unsafe site. HTTPS protects data in transit, but it doesn’t prove the store is legitimate—use the other checks below too.
If you do see a padlock icon, it is a second indicator of an SSL. In some cases, your browser may truncate the front end of an URL, hiding both the padlock and the HTTPS indicators. In this case, copy and paste the URL into another document to check for these indicators if you’re unsure.
You can see this in action on WordPress.org:
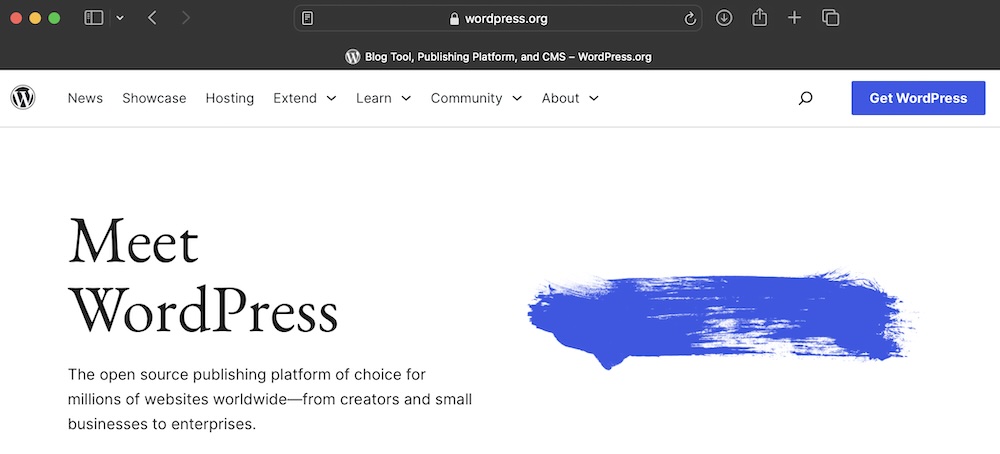
In the address bar, you can see a padlock or site controls icon, at the left of the URL. You can click on the URL to expand it and see the “HTTPS”.

Using a Google Chrome browser, you can click the toggles icon to the left of the URL to see even more information. Once opened, clicking on the lock icon shows this:
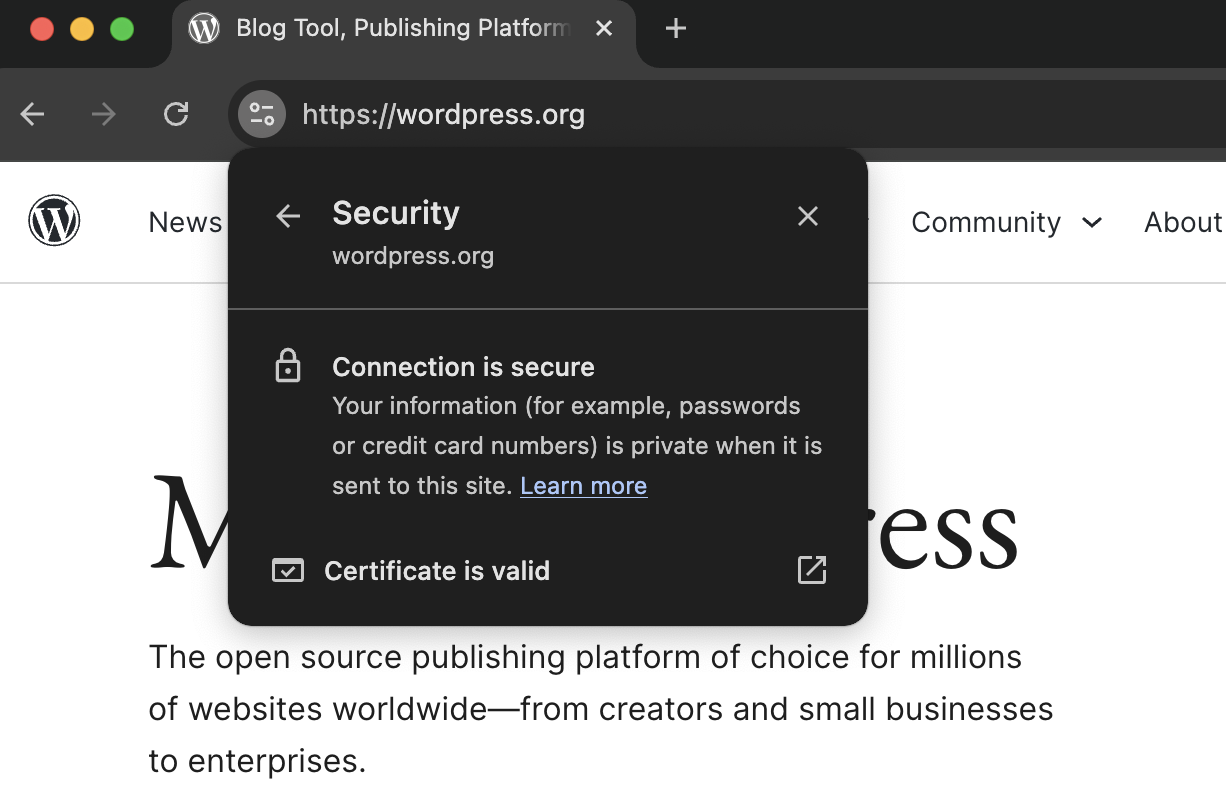
3. Consider the overall appearance of the site
Real businesses with real websites will try to curate a professional appearance with clean, attractive design and error-free text. If the site looks thrown together or sloppy, it’s a warning sign that the site might not be legitimate.
4. Check for the presence and relevance of trust seals
While security badges and trust seals make visitors feel more at ease, be aware that scammers can easily insert these graphic elements onto their sites as well. If you’re unsure about a site’s legitimacy, click on the seal. Real ones should be linked to their source and display security authentication of some sort.
5. Locate and read the security and privacy policy
Real websites will have clearly-defined security and privacy policies available for review. These are often found in a site’s footer. Some sites will also display information about the use of cookies. For example, tennis player Rafael Nadal’s website has a cookie opt-in that appears at the bottom of the screen as soon as the homepage loads.

6. Verify contact information and physical address
Although many cybercriminals will pose as legitimate companies by using realistic-looking logos, designs, and branding images from real businesses, they won’t typically provide contact information. Another giveaway can often be revealed in the details of the URL where spelling errors or nonsensical strings of letters will replace actual business names.
7. Check website reviews and ratings
If the business is unfamiliar, take some time to check reviews, ratings, and other online feedback tied to that product, company, or website. Often scammy sites are clearly tagged by third-party watchdog organizations. A site like Trustpilot is a good resource for checking on the validity of websites.

8. Be wary of sites with many popups and popunders
These intrusive messages are designed to lure visitors into clicking on dangerous links or downloading malware. Don’t just avoid the popups. Instead, leave the site altogether.
9. Verify the age and ownership of the domain
Just like crimes committed in the physical world, cyber bad actors must constantly stay on the move to avoid long-term detection. That means many scam sites are quite new. Taking a moment to check how old a suspicious site is can give you some insight into whether it’s safe to browse or buy from. You can use any domain age checker for this task, but the aptly named Domain Name Age Checker is a good choice.
10. Check how the site accepts payment (and avoid risky methods)
If a store pushes payment methods that are hard to reverse (wire transfer, gift cards, crypto, or “friends & family” transfers), treat it as a major red flag. Prefer credit cards because they typically offer dispute/chargeback protections if something goes wrong.
11. Run the site through a malware/phishing status check (60 seconds)
Before you buy, check whether the site has been flagged for malware or phishing. Use Google’s Safe Browsing site status tool to see if Google is currently warning users about it. If the site is flagged, don’t proceed.
12. Validate the “real business” signals (not just the website)
A legitimate store usually has consistent business details across multiple sources: matching company name, address, phone number, and policies. Red flags include an address that maps to a random location, a support email on a free domain, or policies that look copied/pasted and don’t match the brand. If you can’t confirm who operates the store and how to reach them, don’t buy.
Safe browsing practices for users
Now that you have a clearer idea of the things to look out for when browsing a website — and what might signal a scam — you can move on to the next step. Here are some tips for browsing the web safely as a site visitor or user:
Create and manage strong, unique passwords
Most sites today suggest that new users create strong passwords that are hard to guess or hack. Random password generators and storage systems like 1Password are readily available to help you do just that — and store all of those unique passwords.

Then, establish a schedule to change your passwords on a regular basis.
Use antivirus and anti-malware software
You can automatically scan your computer for viruses or malware using antivirus software. In fact, proactive tools will warn you that you may be doing something dangerous and allow you to opt-out of that behavior before any harm occurs.
For instance, if you attempt to download a file from a website, the antivirus software can scan it before the download occurs, protecting your site from infection. Be sure to heed any automated warnings.
Recognize and avoid phishing attempts and scam websites
Sometimes, you’ll receive an email from what looks to be a legitimate company, except they’re asking for login details or personal information. This should immediately cause suspicion
Legitimate businesses won’t request this information outside of a standard form — and never by email. If you’re ever in doubt, close out of a suspicious site, don’t click any links or download any files from an email, and reach back out to the real organization to double check the request. Customer support for a real company definitely wants to know if scammers are spoofing their site or email address, so reaching out is always recommended.
Update browser software
Computer and software companies are on a never-ending quest to fight against the newest scams and malware. It’s critical to stay up to date on patches and protections as they’re released. Add a reminder to your monthly calendar to check for browser updates to ensure this task doesn’t slip through the cracks.
Be cautious of public Wi-Fi networks
Whether you’re checking your email at a hotel or logging in at a library or coffee shop to do a little work, be very careful of these open Wi-Fi networks that don’t encrypt your personal information. If you must log in on a public network, you may want to change your password once you’re finished to protect the long-term integrity of your account.
Check for website legitimacy before making a purchase
Anytime you are about to enter payment information, double check that the storefront is legitimate. Be sure the payment screens are encrypted and that the site has security measures in place to protect your account. Think of the signals discussed earlier, like a URL with “https” and a padlock icon.
How website owners can enhance site security
Now that you’ve learned what consumers can do to protect themselves, you can move on to discovering how website owners can play their part. If you want to maintain a strong and trusted reputation with your customers and visitors, these measures will solidify your commitment to site security.
| Security Layer | What It Does | Why You Need It |
| Secure Hosting | Provides a secure server foundation for your site. | The first line of defense against infrastructure attacks. |
| SSL Certificate | Encrypts data between the user’s browser and your site (HTTPS). | Essential for protecting login details and payment information. |
| Security Plugin | Filters malicious traffic before it reaches your site. | Proactively blocks common attacks like SQL injections and XSS. |
| Regular Updates | Patches vulnerabilities in WordPress core, themes, and plugins. | Hackers exploit known vulnerabilities in outdated software. |
1. Choose a secure web hosting provider
Internet security requires multiple layers and selecting a trusted hosting provider is the first level of protection. An excellent web hosting provider ensures that proper security measures — like SSL, malware scanning, and encryption — are in place to shield your data and your visitor information from would-be hackers.
2. Implement security certificates
SSL/TLS certificates position organizations to establish a secure connection between their website and those who visit them. It uses a standard protocol that creates encrypted connections between websites and browsers. This is especially important if you request personal information including names, credit card numbers, and phone numbers from your customers. Learn how to obtain a free SSL certificate for your website.
We guard your site. You run your business.
Jetpack Security provides easy‑to‑use, comprehensive WordPress site security, including real‑time backups, a web application firewall, malware scanning, and spam protection.
Secure your site3. Install a robust security plugin
If you manage a WordPress site, your next move should be a dependable WordPress security plugin. Jetpack Security is one of the most trusted options in the industry.

Jetpack Security includes real‑time backups, a web application firewall (WAF), automated malware and vulnerability scanning, and spam protection, all for just $9.95 per month.
4. Update and patch software
Site admins should always stay on top of the latest scams and malware to ensure a site’s protection. This means keeping up with the most recent updates and patches to your site’s software.
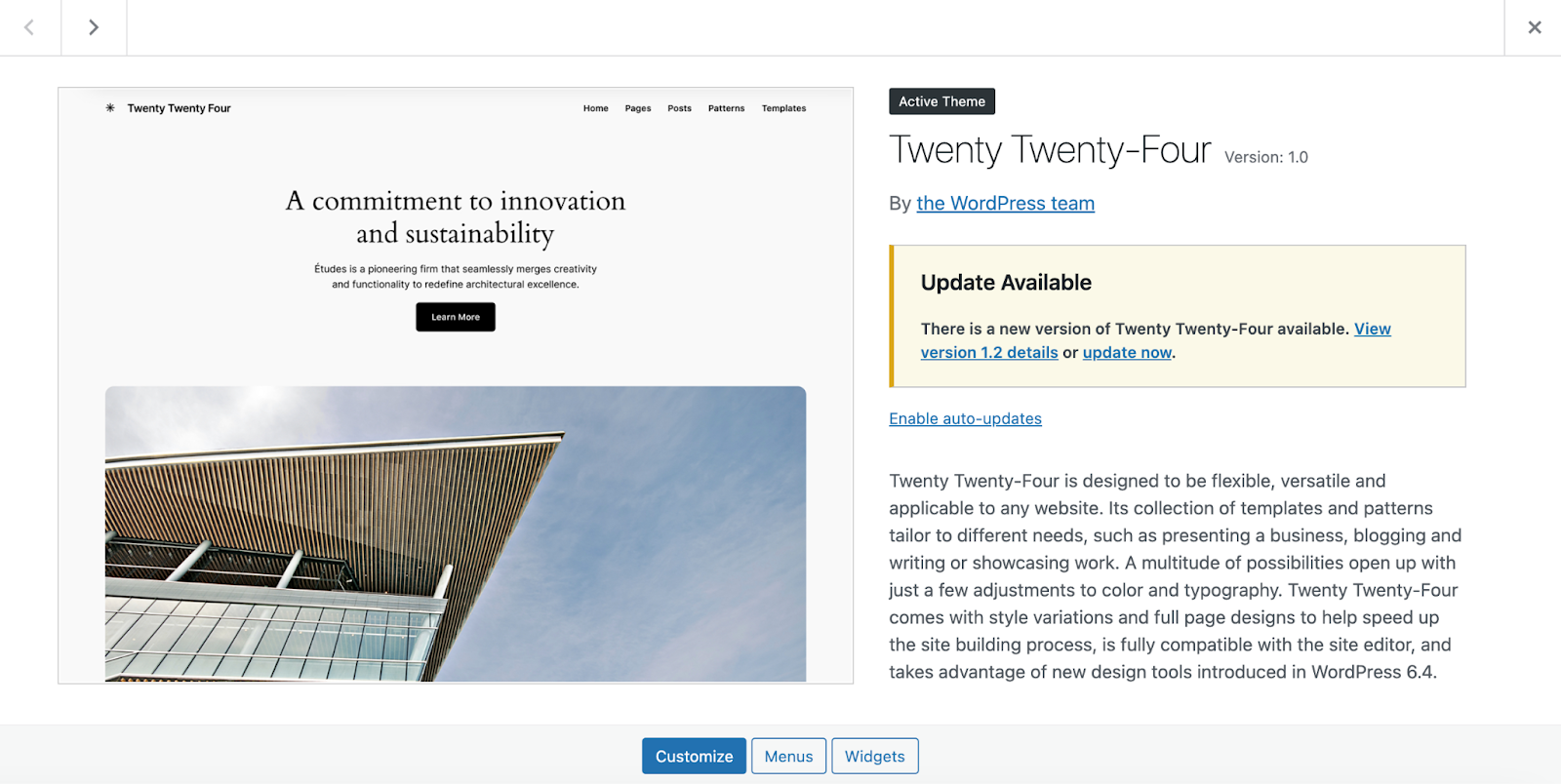
WordPress users can keep track of available updates in their dashboard. Simply go to Dashboard → Updates.
You can also turn on auto-updates to save time and help you remember to upgrade to the latest version. For plugins, simply navigate to Plugins → Installed Plugins and click the Enable auto-updates button to the right of each tool.

You can do the same thing for themes by going to Appearance → Themes and expanding your active theme. Underneath the name, you’ll find Enable auto-updates.
5. Use strong authentication methods
Just as individuals should strive for strong and unique passwords, the authentication methods used by companies should also be as strong as possible and frequently updated. Make full use of two-factor authentication to reduce brute force attacks and other hacking attempts. .
Thankfully, brute force protection is included in Jetpack Security, and you can use Secure Authentication to require two-factor authentication for all users.
6. Conduct regular security audits and penetration testing
Make it a point to conduct regular checks on your site’s overall security system. Working to find your own weak spots gives you time to strengthen those areas before malicious actors find them. If you have a large ecommerce site, a penetration testing tool could come in handy.
7. Clearly display contact information and a privacy policy
Displaying contact info and a privacy policy prominently gives your visitors, prospects, and customers peace of mind. And it helps ensure everyone understands your policies up front.
8. Educate staff on security best practices
Finally, as a website owner, you have an obligation to your customers and visitors and those working on your team. So, be sure to communicate all the above “user” guidelines to your team so they don’t inadvertently put your site and business at risk.
Frequently asked questions
You hopefully now have a better understanding of how to know if a website is safe to browse and buy from. But if you’re still unsure, the following answers to the most commonly asked questions should get you up to speed:
What is HTTPS, and why is it important for website security?
HTTPS stands for “Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure” and is a designation found at the front of a URL. It’s an indication of a website’s security and is one of the easiest ways to know if it’s safe to browse.
What are the risks of shopping on websites without HTTPS?
Shopping on websites that lack HTTPS allows data to be transmitted between a browser and a website without encryption. This puts information like credit card numbers, personal details, and passwords at risk.
How can I tell if a website has a valid SSL certificate?
You can easily tell if a website has a valid SSL certificate by checking its URL to see if it has the HTTPS designation and whether there is a padlock icon. If you don’t see these immediately, copy and paste the URL into a word processing program to see if it’s hidden. You can also check the security certification, which should be available for inspection.
Can a site with HTTPS still be a scam?
Yes. While HTTPS is a crucial security layer that encrypts your data, it does not guarantee the website owner’s integrity. Many phishing sites now use SSL certificates to appear legitimate. That’s why you must combine the HTTPS check with other methods, such as verifying the domain age and checking for credible contact information.
Why is it important to use strong, unique passwords for each website?
It’s understandable why it’s tempting to reuse the same password for multiple websites. After all, it takes work to keep track of so many complex passwords. But, this practice increases your vulnerability to hackers because, once one password is discovered, hackers can then access more than one of your accounts.
What are the benefits of using a password manager for both consumers and website owners?
A password manager enhances security for users by generating and storing strong and unique passwords. This reduces the risk of breaches while also simplifying login processes. For website owners, password managers decrease the likelihood of security incidents caused by compromised user accounts.
What is two-factor authentication (2FA) and how does it enhance security?
Since two-factor authentication requires two channels to ensure users are who they say they are, it can boost security significantly. Typically, a user will be asked for a password or PIN in one channel, like on a standard login screen, and then be required to enter a code that’s sent via email or SMS to verify their identity.
How can I verify the authenticity of trust seals on a website?
To confirm a trust seal’s authenticity, click on it to see the actual trust certificate. Be sure that the site’s URL and name matches the information on the trust certificate.
What should I look for in a website’s privacy policy?
A website’s privacy policy should communicate what kind of data is collected, the methods used, and the purpose of collecting the data in the first place. You’ll want to understand whether the data is shared and what rights you have in accessing and correcting it. A privacy policy should also outline the company’s security, retention, and tracking policies.
How do I recognize a secure payment gateway during an online purchase?
You have several options to recognize a secure payment gateway before you make an online purchase. First, be sure you see HTTPS or a padlock icon in the URL. Second, be sure the site is using well-known payment processors. Third, check the SSL certification link and review contact and refund policies. And finally, be sure that the site isn’t redirecting you to an unknown site for payment processing.
Why should I avoid using public Wi-Fi for online transactions?
Public Wi-Fi networks are often unsecured, making it easier for hackers to steal personal data. They are also more susceptible to fake hotspots set up by attackers to steal your information. Even on legitimate networks, shared connections increase the risk of unauthorized access.
What are the most reliable third-party review sites for checking a website’s reputation?
Trustpilot provides user reviews on various businesses, including ecommerce sites, and is a well-known third-party organization. The Better Business Bureau is known for its detailed business ratings and customer complaints. Sitejabber is another option that aggregates user reviews and ratings specifically for online businesses. Both Google and Yelp offer a broad range of customer feedback on companies and websites, too.
How often should website owners conduct security audits?
Experts recommend quarterly security audits to search for vulnerabilities. However, high-traffic sites or those that have recently made significant site changes may want to conduct them more frequently. Additionally, audits should be conducted after any security incidents or breaches to confirm that all vulnerabilities were identified and resolved.
What is a web application firewall (WAF) and why is it important?
A WAF works to protect web applications by monitoring and filtering traffic between a web application and the internet. A WAF can help defend against common threats such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and other application-layer attacks. Tools like Jetpack WAF work by analyzing incoming traffic for malicious patterns then blocking harmful requests before they reach the web application
How can I protect my website’s backend from cyberattacks?
To protect your site’s backend from attack, you need to put a comprehensive security program in place. This should include:
- Requiring strong, unique passwords
- Requiring the use of 2FA
- Restricting access by using IP allowlisting
- Regularly updating software and plugins
- Scanning for malware and vulnerabilities
- Using a WAF to filter malicious traffic
- Conducting regular security audits to identify and address potential threats.
What types of tools are recommended for enhancing website security?
Several of the tools discussed today can help you enhance your website security. A WAF can filter and monitor your traffic and block malicious requests. Anti-malware software can find and delete malicious code. SSL/TLS certificates ensure that data is encrypted during transmission.
And you should regularly back up data so in case your site is ever compromised it can be restored easily. Jetpack VaultPress Backup is a good option for this.
Jetpack Security: The fast and easy way to secure your WordPress site
While many tools and processes can boost the security of a website, WordPress users should opt for Jetpack Security as an easy‑to‑use, comprehensive solution to common security issues. With real‑time backups, a web application firewall, malware scanning, spam protection, and more, it’s truly a comprehensive safeguard for your whole site.
We guard your site. You run your business.
Jetpack Security provides easy‑to‑use, comprehensive WordPress site security, including real‑time backups, a web application firewall, malware scanning, and spam protection.
Secure your site